Most Of The Body's Energy Reserves Are Stored In The Form Of
Excess glucose can be converted into glycogen the storage form of glucose in animals. Get Results from 6 Engines at Once.
The Body S Energy Systems Trilifeusa
When Glucose Is Stored.

Most of the body's energy reserves are stored in the form of. A Much more energy is stored in the body in the form of carbohydrate than in the form of fat. Specifically the body burns fat after first exhausting the contents of the digestive tract along with glycogen reserves stored in liver cells and after significant protein loss. Most energy stores for the body are in the form of _____ and stored in _____.
C Fat cannot provide all of the energy required for high-intensity muscular activity because the rate of energy release from fat is too slow. Therefore glycogen is the actual energy storage. Carbohydrates are stored in the body in the form of glucose or glycogen.
Get Results from 6 Engines at Once. Energy gates must be felt directly with the mind in your body for they are part of your subtle energy body. Solved Most of the bodys energy reserves are stored in the form of A glycogen.
Lipids as an Energy Reserve. Muscle cells can also store glucose as glycogen the other two-thirds but muscles hoard most of their supply using it just for themselves during exercise. This means a 100m Sprint can be almost completely performed using this energy storage.
One way the body stores fat involves the body transforms carbohydrates into glycogen that is in turn stored in the muscles for energy. Our bodies reserve fuel for a rainy day. Many gates are located at joints or more precisely in the actual space between the bones of a joint.
Adipose tissue B glycogen. Whereas carbohydrates provide a readily available source of energy lipids function primarily as an energy reserve. Swimming movement comes from muscle contraction.
Ad Search Compare The Electricity Market. Adipose tissue D triglycerides. These triglycerides that are stored in the form of energy reserves reside primarily in adipose tissue which has the additional function of insulating your body and protecting internal organs from.
However glycogen is not the only energy storage used in muscles. The amount of lipids stored as an energy reserve. The concept of energy gates has been passed down from ancient China originally worked out by the Taoists.
All energy for muscle comes from inputted energy that is derived from food. These molecules are transported through your digestive system and then converted into glucose by the liver to make a usable form of energy for the brain and your muscles. Glucose a major source of bodily fuel is stored in the form of glycogen.
When the muscles reach their capacity for glycogen storage the excess is returned to the liver where it is converted into triacylglycerols and then stored as fat. Carbohydrate fat and protein. Carbohydrates such as sugar and starch for example are readily broken down into glucose the bodys principal energy source.
This energy takes three forms. The brain maintains a small amount of glycogen which is thought to provide an emergency energy reserve during times of severe glucose deprivation. The muscle actually uses a quite clever energy management system.
The average person has about 2500 calories of carbohydrate reservesstored mostly in liver and muscleto use for all kinds of energy-needing functions especially a need for immediate energy like when youre trying to catch a bus or escape a charging rhino. When the body senses a need for more glucose the hormone glucagon is released and. Ordinarily the body responds to reduced energy intake by burning fat reserves and consuming muscle and other tissues.
Energy is the body is stored in five different ways. B Protein is the predominant fuel source during exercise. Skeletal muscle C triglycerides.
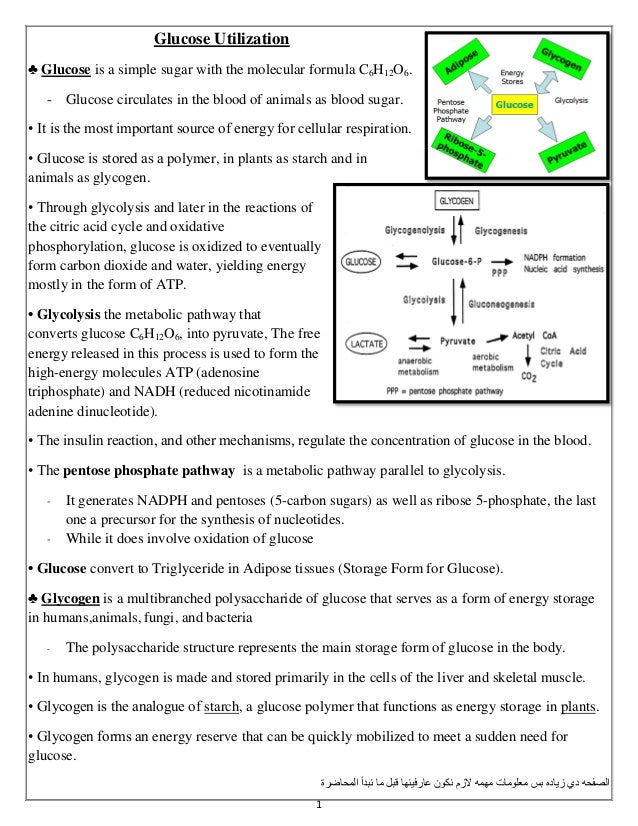
It is a chemical compound stored primarily in the muscle cells that in its chemical breakdown provides energy for cells. During the first 2-7 seconds it uses phosphocreatine or creatine phosphate to quickly replace used ATP as mentioned in the answer by David. The polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the body.
This chemical energy is derived from food carbohydrates fats and proteins stored in the body and ultimately converted into adenosine triphosphate ATP. Glycogen functions as one of two forms of energy reserves glycogen being for short-term and the other form being triglyceride stores in adipose tissue ie body fat for long-term storage. Nearly all of the energy needed by the human body is provided by the oxidation of carbohydrates and lipids.
ATP is the energy molecule that the body uses for work. Ad Search Compare The Electricity Market. See table 21 Estimated Energy Stores in Humans The body can store some of these fuels in a form that offers muscles an immediate source of energy.
ATP Adenosine triphosphate CP Creatine phosphate Glycogen Fat Protein.
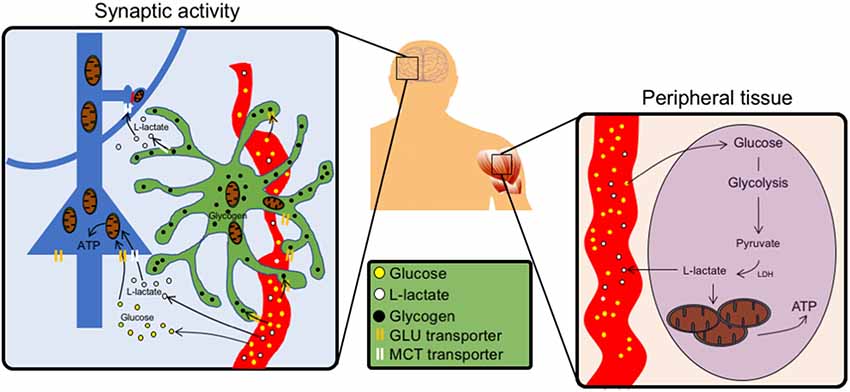 Frontiers The Strategic Location Of Glycogen And Lactate From Body Energy Reserve To Brain Plasticity Cellular Neuroscience
Frontiers The Strategic Location Of Glycogen And Lactate From Body Energy Reserve To Brain Plasticity Cellular Neuroscience
 The Physiology Of Fasting Zero
The Physiology Of Fasting Zero
 Glycogen An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Glycogen An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Carbohydrate And Fat Utilization During Rest And Physical Activity European E Journal Of Clinical Nutrition And Metabolism
Carbohydrate And Fat Utilization During Rest And Physical Activity European E Journal Of Clinical Nutrition And Metabolism
The Body S Energy Systems Trilifeusa
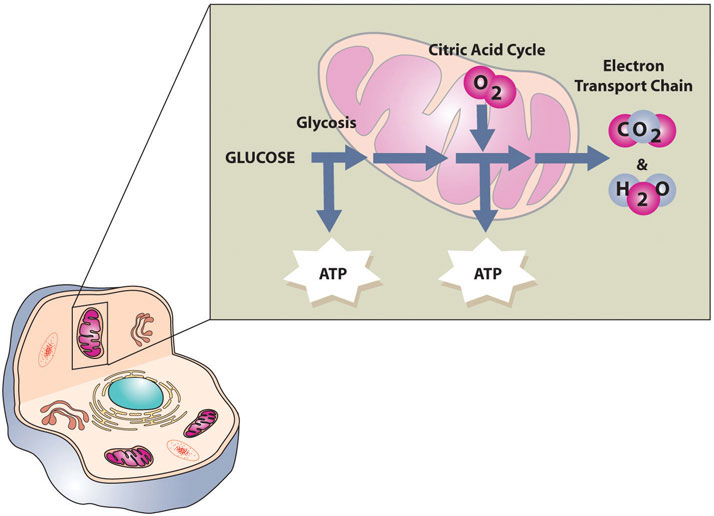 The Functions Of Carbohydrates In The Body
The Functions Of Carbohydrates In The Body

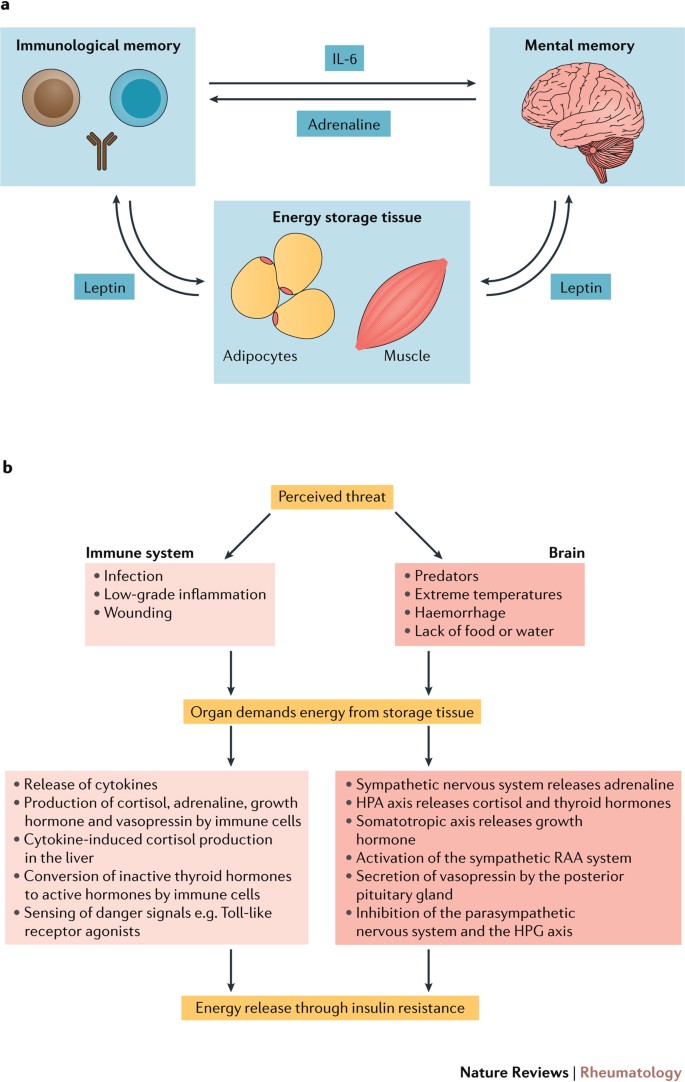 The Brain And Immune System Prompt Energy Shortage In Chronic Inflammation And Ageing Nature Reviews Rheumatology
The Brain And Immune System Prompt Energy Shortage In Chronic Inflammation And Ageing Nature Reviews Rheumatology
The Body S Energy Systems Trilifeusa
 Liver Functions Harry And Jaz Protein Synthesis And Metabolism Ppt Download
Liver Functions Harry And Jaz Protein Synthesis And Metabolism Ppt Download
 Cell Energy Cell Functions Learn Science At Scitable
Cell Energy Cell Functions Learn Science At Scitable
Comments
Post a Comment